Studies in molecular spectroscopy led to the development of the first laser.
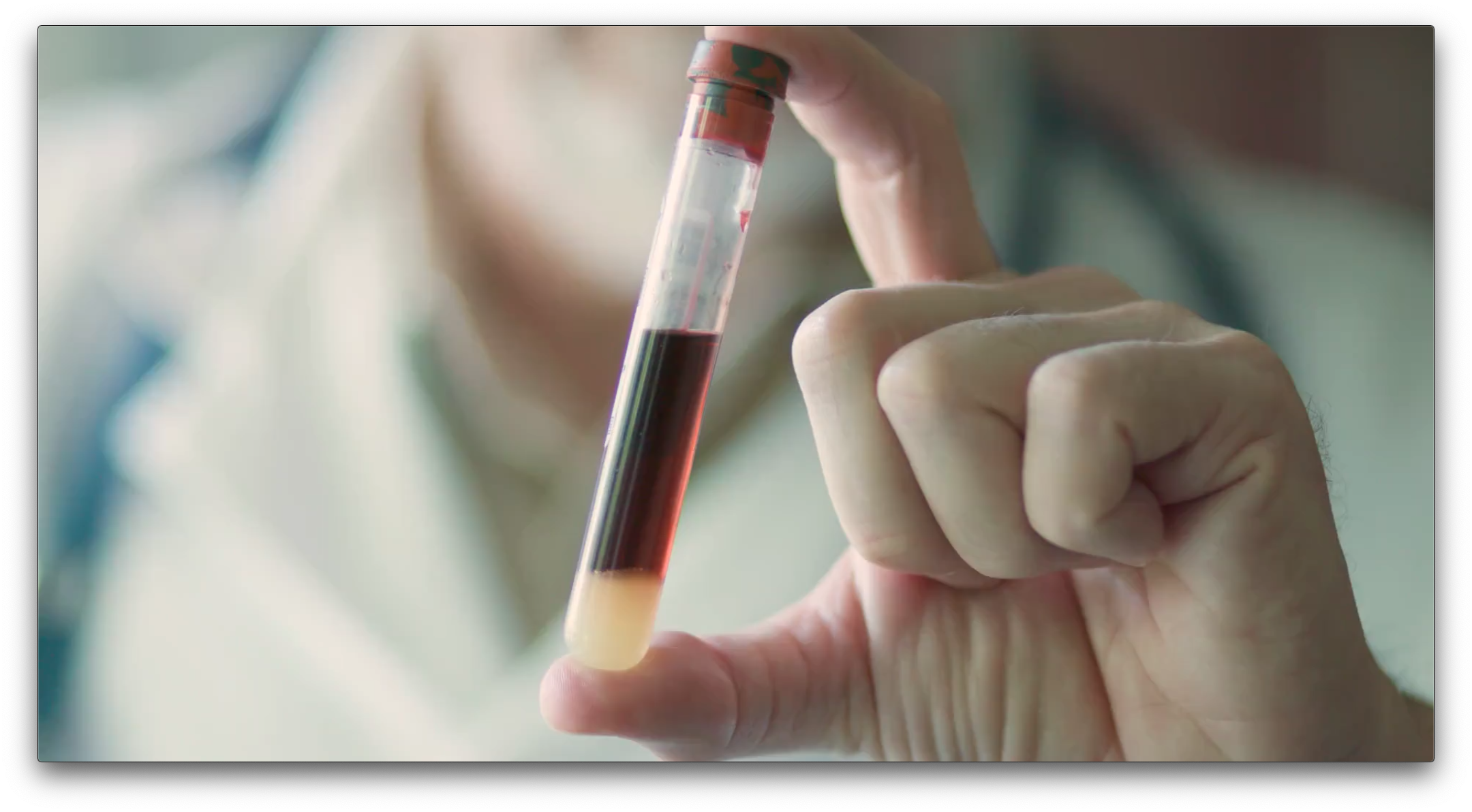
Measurement of toxic compounds in blood samples as well as other forms of blood testing is done using spectroscopy.
The types of spectroscopy are distinguished by the type of radiative energy involved in the interaction. In many applications, the spectrum is determined by measuring changes in the intensity or frequency of this energy. The types of radiative energy studied include:
Electromagnetic radiation was the first source of energy used for spectroscopic studies. Techniques that employ electromagnetic radiation are typically classified by the wavelength region of the spectrum and include microwave, terahertz, infrared, near-infrared, ultraviolet-visible, x-ray, and gamma spectroscopy. Particles, because of their de Broglie waves, can also be a source of radiative energy. Both electron and neutron spectroscopy are commonly used. For a particle, its kinetic energy determines its wavelength. Acoustic spectroscopy involves radiated pressure waves. Dynamic mechanical analysis can be employed to impart radiating energy, similar to acoustic waves, to solid materials.
